Acid is 12 ionised. K a A - H HA The acid dissociation constant is also known as the acidity constant or acid-ionization constant.
Solved Part A Calculate The Acid Ionization Constant Ka Chegg Com
HA H A -.

. Calculating Percent Ionization of a Weak Acid Step 1. α 12 100 012. HF H F-.
HSO 4 H SO 4 2. The larger the Ka of an acid the larger the concentration of and A relative to the concentration of the nonionized acid HA in an equilibrium mixture and the stronger the acid. 13 10 2.
This constant K a is called the acid ionization constant. H O COH l H 2Ol H O CO H 3O. For more details click here.
H 2 SO 4 H HSO 4. 61 10 5. You can measure the strength of an acid by its dissociation constant K a which is a ratio formed by dividing the concentration of products by the concentration of reactants.
Unless an acid is extremely concentrated the equation is simplified by holding the concentration of water as a constant. In a 010-M solution the acid is 29 ionized. Acid Ionization Constants at 25C.
HAc H Ac-. H 2 C 2 O 4 H HC 2 O 4. Ka H Ac- HAc 176X10-5.
H A- HA K a provides a measure of the equilibrium position. This will have an important consequence as we move into solving weak acid. 5 H 3 O 10 p H.
Ka x2 00100 176X10-5. Ka 012 x 000300 x 012 x 000300088 x 000300 000000013000264 492 x 10-5moleL. The larger the value of pK a the smaller the extent of dissociation.
If for example you have a 01 M solution of formic acid with a pH of 25 you can. The ionization constants for sulfurous acid are Ka1 14E-2 and Ka2 63E-8. Answer 1 of 4.
HPO 4 2 H PO 4 3. X is indeed small compared to 00100 so ig. Because the acid is weak an equilibrium expression can be written.
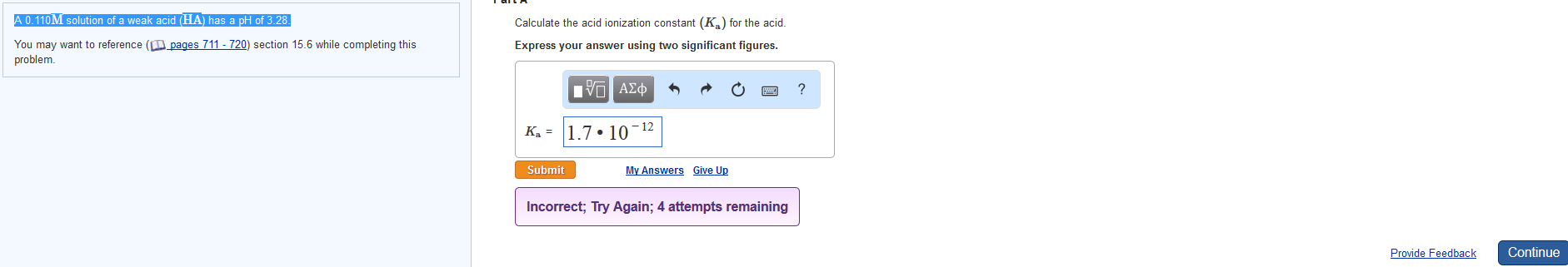
Calculate the acid ionization constant Ka for the acid. PKa log10Ka. Write the balanced dissociation equation for the weak acid.
This site reports that Ka for formic acid 170 105 so it is a weak Bronsted acid. See the answer See the answer done loading. Solving for K a.
Ka Concentration of products Concentration of reactants. 75 10 3. Determine Ka for hydrogen sulfate ion HSO4-.
Ka H A- HA so plug in the values above and you can calculate the value of Ka. Use the concentration of H 3 O to solve for the concentrations of the other products and. Hypochlorous acid HOCl has an ionization constant of 32 10-8.
Ka H O COH 3O H O COH l. Calculate the acid ionization constant Ka for the acidA 0180 M solution of a weak acid HA has a pH of 294. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings.
From the chemical equation above it can be seen that H 3 O and Ac concentrations are in the molar ratio of one-to-one. Then set down the expression for dissociation constant Ka for acid As we have the equation from step 1 now can. So degree of dissociation α is.
K a H30 A-HA All the reactions happen in water so it its usually deleted from the equation. Create an Initial Change Equilibrium ICE Table for the. Name of Acid Ionization Equation K a.
The lower the Ka value the higher the pKa value the weaker the acid. The acid ionization represents the fraction of the original acid that has been ionized in solution. An acid is classified as strong when it undergoes complete ionization in which case the concentration of HA is zero and the acid ionization constant is immeasurably large Ka.
Set up an ICE table for the chemical reaction. 65 10 2. Ka cα2 000300 0122 432 105.
Write the balanced acid dissociationionization reaction Lets firstly write the balanced ionization reaction of. Convert pH to H pH is defined as -log H where H is the concentration of protons in solution in moles per liter ie its molarity. For the reaction of HAaq A- H So upon substitution.
For example acetic acids value is 177 x 10 5. It is more convenient to discuss the logarithmic constant pKa for many practical uses. H F- since for every H ion produced a F- ion will be produced.
For the reaction in which the acid HA dissociates to form the ions H and A -. For weak acid acid dissociation constant Ka is approximately given by. A weak acid has a pK a value in the approximate range of -2 to 12 in water.
Consider the equilibrium ionization of acetic acid HAc. An acid ionization constant K a is the equilibrium constant for the ionization of an acid. Submitted by chrisf on Wed 06252008 - 2254.
The relationship between Ka pKa and acid strength is as follows. Solve for the concentration of H 3 O using the equation for pH. K a the acid dissociation constant or acid ionisation constant is an equilibrium constant that refers to the dissociation or ionisation of an acid.
Often times the K a value is expressed by using the pK a which is equal to latex-log_ 10 K_a latex. In a 010-M solution this base is 00015 ionized. When given the pH value of a solution solving for K a requires the following steps.
Steps in Determining the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH. HA A - H. Suppose that you have a 00100 M solution of acetic acid.
Calculate the ionization constant for each of the following acids or bases form the ionization. The ionization for a general weak acid HA can be written as follows. And we write the equilibrium equation in the usual way.
HC 2 O 4 H C 2 O 4 2. H 3 PO 4 H H 2 PO 4. H 2 PO 4 H HPO 4 2.
H 10 -212 00760 from the pH. X Ac- 420X10-4 M. HF 100 M - H 0924.
It can be determined by experiment and each acid has its own unique value. A 0110 M solution of a weak acid HA has a pH of 333.

Chemistry Acids Bases 28 Of 35 How To Find The Ionization Constant Ka Youtube

Chemistry Acids Bases 28 Of 35 How To Find The Ionization Constant Ka Youtube

18 2 Acid And Base Dissociation Constants Ka And Kb Hl Youtube

Solved Part A Calculate The Acid Ionization Constant Ka Chegg Com
0 Comments